Plastic resins are used to make medical products of all types. This is because it’s inexpensive, lightweight, strong and durable. Plastic injection molding allows for many design options and it’s relatively easy to modify them as needed. Some resins are appropriate for single-use applications and can also be recycled.
But not every type of plastic is safe and effective for every use in a medical or healthcare environment. For this reason, the FDA and other regulatory agencies doesn’t specifically certify any plastic resin, although some types of plastic have proven themselves safe and reliable in many applications.
Therefore a product developer must choose the resin they want to use very carefully based on several important criteria.

Types of Applications
To meet the needs of the medical industry, plastic resins must demonstrate a wide variety of desirable properties. They may need to resist various chemicals, sterilization, radiation or magnetism. Also, they usually should be non-toxic in the presence of body fluids or tissue. And, some resins must be strong and heat resistant, while others must be flexible or disposable.
To help you find the one that is right for you, let’s look at the most common design criteria and the plastic resins that are best suited to fulfill them.

Disposable
These products are single-use and can be safely disposed of without hazard.
Products: Medical forceps, drinking cups, latex gloves, specimen bottles
Materials: Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), nylon, Polyurethane (PU), Nitrile
No Contact
Some products that will be used in a clinical setting such as tools or supporting equipment but that will not be in direct contact with the body.
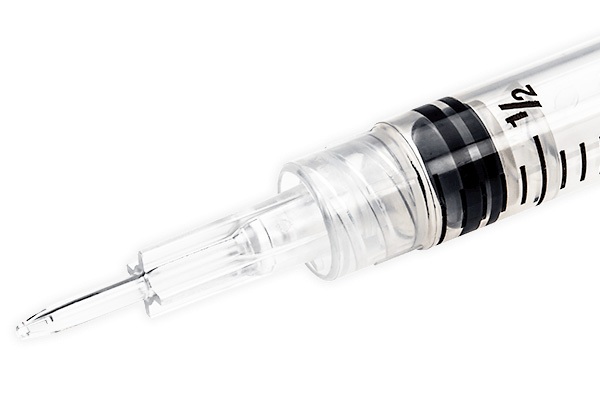
Products: Syringes, tubes, pill dispensers, IV bags, trays, trash containers
Materials: Polyamide (nylon and polyester), polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Low to Medium Contact
Temporary contact or non-invasive products.
Products: Feeding tubes, catheters, surgical instruments, splints, thermometers, oxygen masks
Materials: PEEK, polyurethane (PU), PE, polypropylene (PP), Nylon
Long-Term Contact
Permanent or semi-permanent implants and physical appliances on or inside the body.
Products: Artificial heart valves, pacemakers, artificial joints, hearing aids
Materials: PE, PET, PU, PMMA

Chemical Resistant
These products will normally be cleaned, sterilized and reused many times.
Products: Ventilator tubes and masks, surgical clamps, incubating chambers
Materials: PPSU, PEEK and PC.
Radiation Resistant
X-rays, MRI and chemotherapy treatments can all be a source of radioactive contamination. Since radiation effects are cumulative over the lifetime of a product, it’s important to choose resins that will not degrade.
Products: Machines used in an operating theater, X-ray and other diagnostic equipment.
Materials: ABS, PPSU, PEEK, PU
Drug Delivery
Dispensers that deliver drug dosages must be anti-static so that fine powders and aerosols do not stick to the surface.
Products: Vials, tubes, injectors and other delivery mechanisms for medicines in spray and powder form.
Materials: Acrylic (PMMA), Polypropylene, ABS, PC
Artificial Joints
Joint replacement material for semi-permanent internal use must be strong, non-toxic and low-friction.
Products: Hip joints, finger joints, wrists, etc.
Materials: Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE)
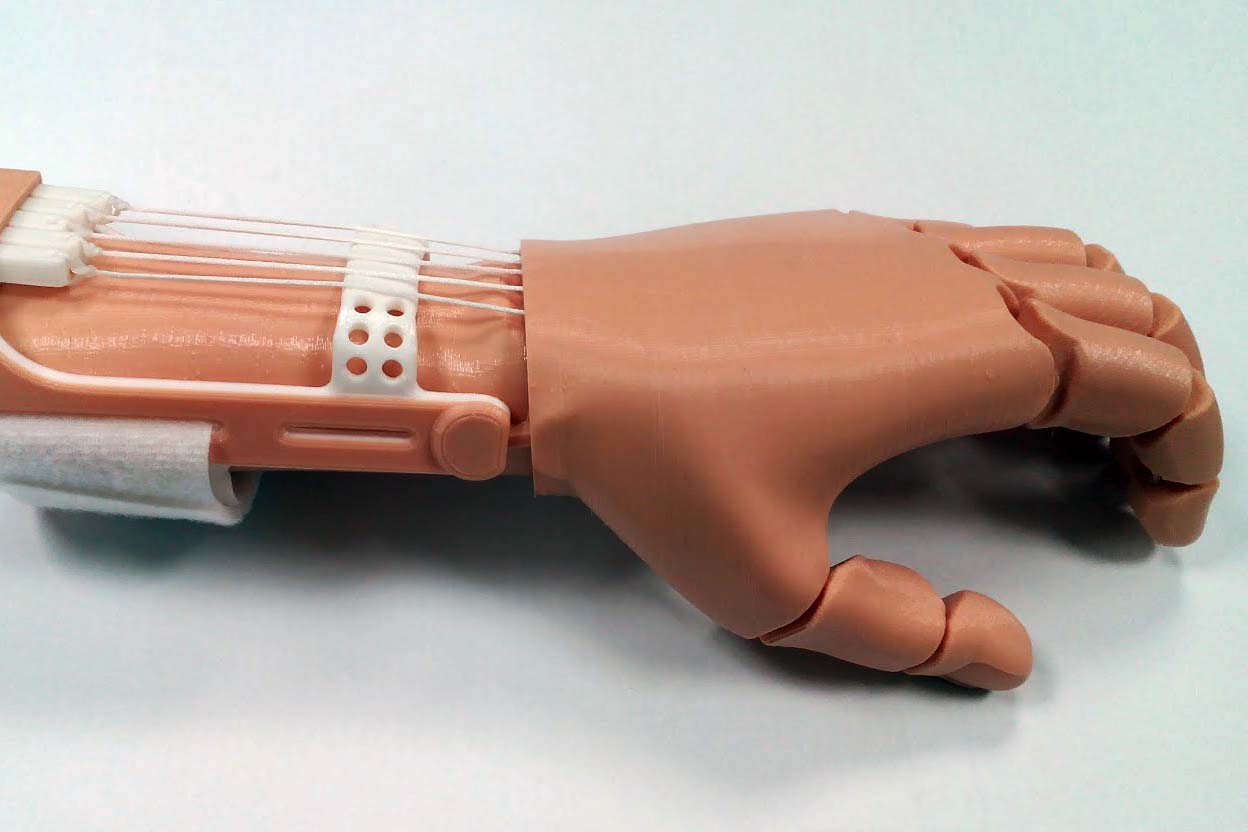
Prosthetics
Artificial limbs should be high-impact, easy to form, strong but not too heavy.
Products: Partial or total limb replacements, orthotics, braces and exoskeletons
Materials: ABS+PC, glass-filled nylon, PMMA, PEEK, POM, High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
Want to learn more?
These are just a few of the many possible uses for plastic resins in medical and healthcare products. Because there are so many variables to consider, let us offer you more specific material and design consultancy on your next project when you contact us for a free quotation.
Star Rapid gratefully acknowledges additional information provided by pmcplastics.com.